Paper as a building material
Natural materials such as wood or paper have been used in the building industry for thousands of years and still play an important role in modern building and interior construction. Examples range from plywood slabs and gypsum fibreboards through to laminates. The available products are mainly based on the experience of the manufacturers. Thereby paper offers excellent potential for bio-based applications in the building industry. It is inexpensive to produce, consists mainly of renewable raw material, offers very good strength properties in relation to its own weight, can be produced as a sheet material but also with high porosity or even as a foam and is relatively easy to chemically functionalize.
Purpose
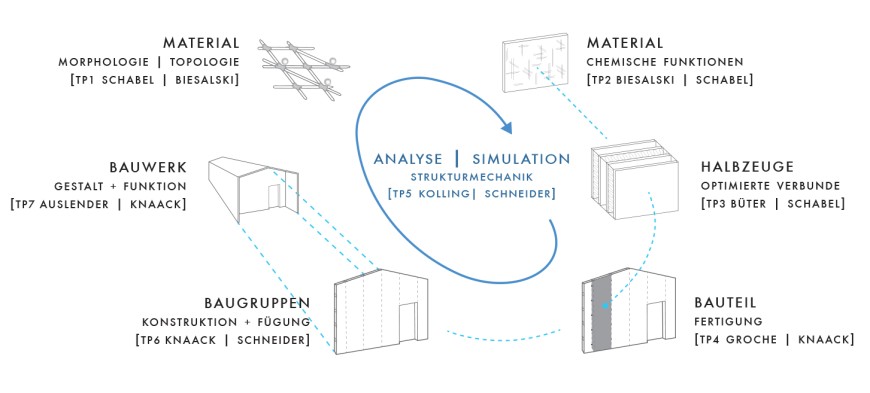
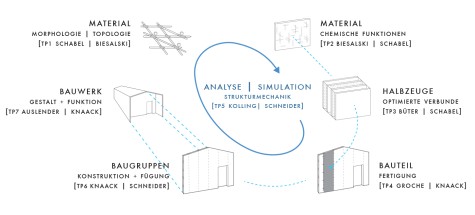
The aim of the proposed focus is to provide scientific and technical foundations for the use of paper in building applications and to develop new approaches to solutions. For this purpose, the material properties of paper have to be adapted to the new requirements and further developed (e.g. high strength, water resistance), the possibilities for individualized shaping with paper materials have to be investigated (e.g. processing in thermoforming processes) and design approaches for the building components and buildings as well as the dimensioning and interpretation are to be worked out. The production of beam and area elements on paper basis will be developed model-wise. This will enable the construction of new structures made of paper to be suitable for materials, production and use by means of scientifically proven methods.
Temporary structures
The focus is on buildings for temporary use (so-called “flying buildings”), which are according to building requirements, if necessary, equipped with smaller technical requirements. Technologies and systems for the production of such structures for uses, such as transitional buildings for commercial purposes or schools, emergency accommodations or one-time major events, as well as for so-called “micro homes” or exhibition stands, have so far been little developed in Germany. However, they represent a greater potential, both for material and construction and the optimized use of resources and financial resources, as the use of sustainable materials and efficient processes plays an important role, especially in temporarily used structures.
Duration: 4 years – 1.01.2017 – 31.12.2020
Budget: 4,6 Mio. EUR
Lead: Technische Universität Darmstadt
Partners: h_da Hochschule Darmstadt THM Technische Hochschule Mittelhessen
Participating institutes and professors
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Samuel Schabel – Chair of Paper Manufacturing and Mechanical Process Engineering (Coordinator), Mechanical Engineering, TU Darmstadt
- Prof. Ariel Auslender – Chair of Plastic Design, Architecture, TU Darmstadt
- Prof. Dr. rer. nat. habil. Markus Biesalski – Chair of Macromolecular Chemistry and Paper Chemistry, Chemistry, TU Darmstadt
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Andreas Büter – Functionally integrated lightweight construction, Mechanical Engineering, Darmstadt University of Applied Sciences
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Dipl. Wirtsch.-Ing. Peter Groche – Chair of Production Technology and Forming Machines, Mechanical Engineering, TU Darmstadt
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Ulrich Knaack – Chair of Facade Technology, Building and Environmental Sciences, TU Darmstadt
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. Stefan Kolling – Institute of Mechanics and Material Research, Mechanical Engineering, Technische Hochschule Mittelhessen
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jens Schneider – Chair of Statics, Building and Environmental Sciences, TU Darmstadt