Correlating changes of the unit cell parameters and microstructure with magnetic properties in the CeFe11Ti compound
2021/02/16
F. Maccari, S. Ener, D. Koch, I. Dirba, K. P. Skokov, E. Bruder, L. Schäfer, O. Gutfleisch
Journal of Alloys and Compounds 867, (2021).
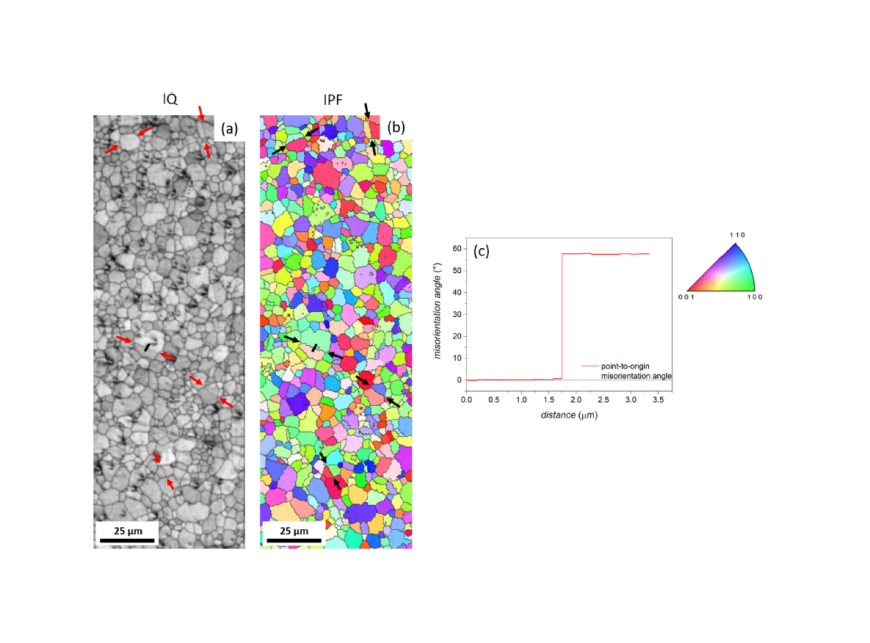
The criticality of rare-earth elements and its impact on the permanent magnet market have initiated a search for alternative material systems, either to fill the magnetic performance gap between ferrites and Nd-Fe-B magnets or to even replace the existing benchmark systems. Ce-based systems are attractive due to the abundance of cerium, however the formation of secondary phases leads to challenges for Ce-based compounds. We investigated the formation and magnetic properties of ThMn12-type Ce1+xFe11Ti samples for x = 0.15 and 0.20 compositions. Microstructural investigations reveal the formation of twin boundaries in the ThMn12 grains with a misorientation angle of 58∘ ± 2∘. By varying the chemical composition and lowering the annealing temperatures, a grain refinement and reduction in twin boundary density was achieved. In addition, the magnetostrictive characteristic of CeFe11Ti-phase was investigated. Around the Curie temperature, an M2 behaviour is noted, in contrast to an M3 behaviour at lower temperatures. To probe the effect of unit cell compression and expansion on the magnetic properties, magnetic characterizations were carried out under hydrostatic pressure and after hydrogenation. A slight reduction is observed for the measured anisotropy field under 0.45 GPa hydrostatic pressure in the temperature interval of 10–300 K, which is consistent with the small increase detected for the hydrogenated compound.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.158805



