Motivation and Objectives of Subproject 2
Paper has unique chemical and physical properties that makes it very interesting as a construction material. TP2 focusses on chemical functionalization of paper to obtain tailor made material properties. These properties are mainly moisture, fire and microbial protection.
Nowadays, there are already paper materials that meet such requirements, but these materials have some problems which renders them unsuitable for use as a construction material. In the case of paper laminates, for example, development of both materials typically occurs independently of one another. As long as the individual materials are not chemically bonded, there may always be a possibility of delamination of the coating. Furthermore, a barrier layer is created which closes the pores of the building material and thus can prohibit or negatively influence the adhesion of other materials. In addition, the recycling of these materials is not trivial since the functional elements, such as halogenated hydrocarbons, used for flame retardancy have to be recycled and disposed through specialized processes.
In TP 2, a material will be developed, which addresses the aforementioned limitations of existing technology. Likewise, the chemical modification of the fiber interface can have a positive effect on the mechanical properties of the paper in order to improve the production of components and semi-finished products. The focus here is not on the further development of the functional laminates but on the chemical modification of the fiber interface itself. The core questions of the project are, whether the moisture and fire protection properties can be achieved by means of the corresponding chemical functionalization of the fiber surface. Furthermore, the latter must possess a certain thermal and mechanical stability, in order that the produced materials endure the subsequent forming processes and the production of semi-finished products. In addition, the materials produced must meet the requirements of the different fields of application.
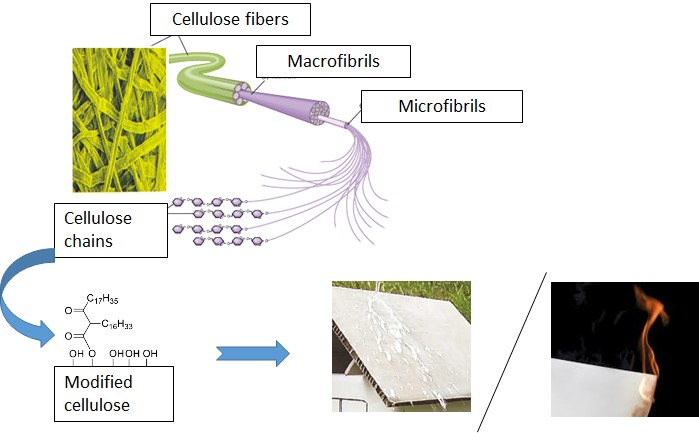
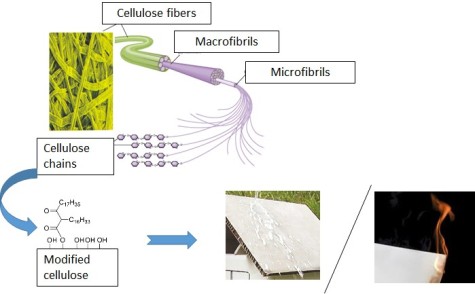
Chemical functionalization of the fibers for moisture protection
Within subproject 2 fibers, which are used for the production of papers, are chemically modified, so that they have hydrophobic or water-repellent properties. Care should be taken that these modifications are covalently attached to the fibers in order to reduce the occurrence of defects. Furthermore, the influences of the modified fibers on the properties of the papers formed therefrom are investigated.
Chemical functionalization of the fibers for fire protection
In addition to the moisture protection of the fibers, the combustibility of the paper should be reduced. This is to be done with the help of fire protection materials, which are incorporated into the paper. The aim is to develop a non-toxic, halogen-free and biodegradable fire protection system, which meets the requirements of the BAMP project.
Multifunctional properties
In addition to the protection against moisture and fires, there are other influences that can adversely affect the properties of paper, thus minimizing the durability and stability of the paper house. One of these influences is microorganisms such as bacteria or mold. Against these factors antimicrobial materials are to be incorporated into the paper or be applied via the preceding functionalizations.


