Motivation and Objectives of Subproject 4
In the field of construction industry individualized parts became state of the art as façade elements. Currently, the shaping of these elements leads to high investments in tools and plants. In contrast to already existing proceedings for the forming of metallic components, there is no technology for the individualized shaping of paperboard available. Therefore, it is the aim to develop an efficient process chain for an individualized shaping of paperboard. Beside paperboard, sandwich structures will be investigated, since they have a good weight-specific bending stiffness as well as a high noise and heat insulation. However, current sandwich structures have a mineral oil-based core. To reduce the use of limited resources, sandwich structures with a paper-based core and aluminum face sheets will be developed within the subproject 4 to increase the sustainability of sandwich structures. One main aspect of this development is the faultless manufacturing of shaped and cut sandwich structures.
Since the recycling process has a high impact on the sustainability, the separation of the single layers will be also investigated within the project.
Technology development
As illustrated in Figure 1 the process chain to be developed can be divided into three parts:
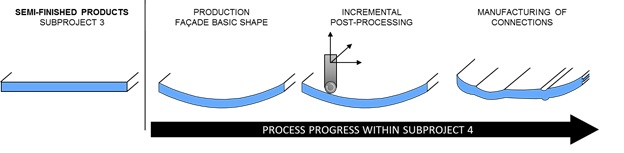
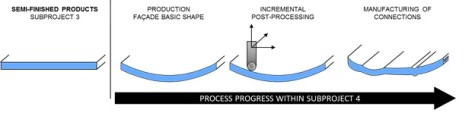
Based on the plane, semi-finished products provided from subproject 3, a basic 3D-shape will be manufactured. With the collaboration of all subprojects a basic shape is specified. Since a high form flexibility and a superimposition of pressure, leading to larger elongation values, a hydroforming tool concept is pursued.
Beside the development of a hydroforming tool concept for the basic shape, the incremental forming is adjusted to the requirements of paperboard forming. Within the process chain it allows to individualize the basic shape or to form unique parts, for which solid tools are too expensive.
Joints
Following the forming processes the components have to be trimmed. Additionally, connections have to be manufactured by shear cutting or milling. Especially the design of the connections will be treated in close collaboration with the subprojects 5 and 6.
Experimental investigation of process parameters
Within subproject 4, the influence of the process parameters of hydroforming and incremental forming on the deformation limits of paperboard and paper-based sandwich structures is investigated. Due to the diverse parameters such as material composition, temperature, moisture and deformation speed extensive tests series have to be performed.
Numerical mapping of the forming processes
The process design is supported by numerical simulations. Beside the aspect of cost saving, the numerical models will be used to design further processes with different types of paperboard as well as for a better understanding of the effective forming mechanisms. Additionally to the numerical process simulation, experimental methods will be developed to determine the plastic forming mechanisms of paperboard.
Component testing
Next to the process development, test methods will be investigated with regard to their usability for a non-destructive component testing. Based on former projects, thermography and computed tomography are promising methods. While thermography is primarily useable for large scaled parts, computed tomography enables the detection of small faults on small parts.


