The main goals of this project are proposing kinetic models for the thermo-chemical oxidation/reduction of iron particle, and iron dust firing investigations in a CFD environment. First, the kinetics of the reduction of hematite to iron will be investigated. Then, the kinetic of the reverse (oxidation) step will be studied, bringing further considerations, such as the type of oxidation, or the heat release. Finally, the kinetic models will be transposed in a CFD environment for the simulation of iron flames, from a laminar case (Bunsen burner) to a turbulent one (high-pressure jet). Ultimately, this sub-project lays the basis for the accurate assessment of the dust firing efficiency.
Scientific questions:
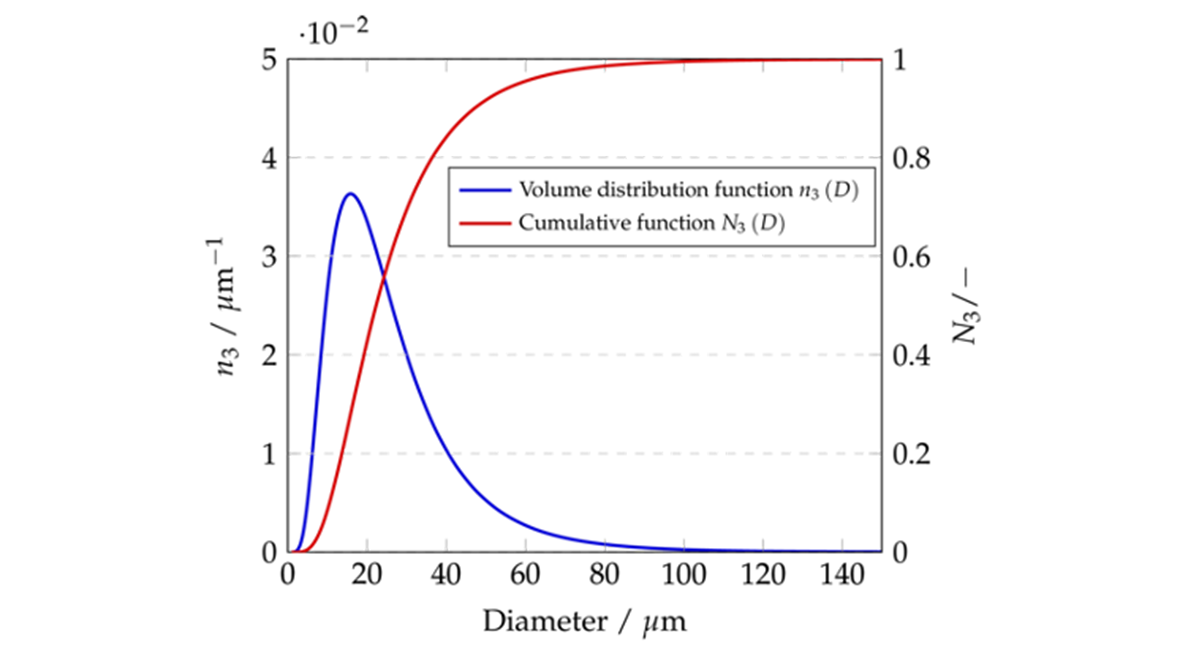
- How does the overall reduction/oxidation of a single particle evolve with time for a variety of gas conditions (temperature, pressure, composition, …) and solid ones (size, porosity, composition, …)?
- How does the macroscopic flame structure evolve with varying gas to fuel ratio, particle size or temperature?
- What are the effects of turbulence on iron dust oxidation?
- What efficiency can be expected in an industrial reactor of iron thermo-chemical oxidation?